 Finance is the life blood of business. It flows in mostly from scale of goods and services. It flows out for meeting various types of expenditure. The activating element in any business which may be on industrial or commercial undertaking is the finance.Business finance has been defined as those activities which have to do with the provision and management of funds for the satisfactory conduct of a business. Business finance is defined as that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of business enterprise.So we can say business finance is mainly developed around three major objectives. Firstly, to obtain an adequate supply of capital for the needs of the business, Secondly, to conserve and increase the capital through better management, Thirdly, to make profit from the use of funds which is an overall objectives of a business enterprise.Before industrial revolution, finance was not of much importance. The methods of production were simple. For example, the artisan used to work in open small hut. He had simple tools mostly made by himself. Labour at that time was more important than capital and finance did not pose any problem. Production in those days was, therefore labour intensive.
Finance is the life blood of business. It flows in mostly from scale of goods and services. It flows out for meeting various types of expenditure. The activating element in any business which may be on industrial or commercial undertaking is the finance.Business finance has been defined as those activities which have to do with the provision and management of funds for the satisfactory conduct of a business. Business finance is defined as that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of business enterprise.So we can say business finance is mainly developed around three major objectives. Firstly, to obtain an adequate supply of capital for the needs of the business, Secondly, to conserve and increase the capital through better management, Thirdly, to make profit from the use of funds which is an overall objectives of a business enterprise.Before industrial revolution, finance was not of much importance. The methods of production were simple. For example, the artisan used to work in open small hut. He had simple tools mostly made by himself. Labour at that time was more important than capital and finance did not pose any problem. Production in those days was, therefore labour intensive.Friday, December 25, 2009
Finance and its importance
 Finance is the life blood of business. It flows in mostly from scale of goods and services. It flows out for meeting various types of expenditure. The activating element in any business which may be on industrial or commercial undertaking is the finance.Business finance has been defined as those activities which have to do with the provision and management of funds for the satisfactory conduct of a business. Business finance is defined as that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of business enterprise.So we can say business finance is mainly developed around three major objectives. Firstly, to obtain an adequate supply of capital for the needs of the business, Secondly, to conserve and increase the capital through better management, Thirdly, to make profit from the use of funds which is an overall objectives of a business enterprise.Before industrial revolution, finance was not of much importance. The methods of production were simple. For example, the artisan used to work in open small hut. He had simple tools mostly made by himself. Labour at that time was more important than capital and finance did not pose any problem. Production in those days was, therefore labour intensive.
Finance is the life blood of business. It flows in mostly from scale of goods and services. It flows out for meeting various types of expenditure. The activating element in any business which may be on industrial or commercial undertaking is the finance.Business finance has been defined as those activities which have to do with the provision and management of funds for the satisfactory conduct of a business. Business finance is defined as that business activity which is concerned with the acquisition and conservation of capital funds in meeting the financial needs and overall objectives of business enterprise.So we can say business finance is mainly developed around three major objectives. Firstly, to obtain an adequate supply of capital for the needs of the business, Secondly, to conserve and increase the capital through better management, Thirdly, to make profit from the use of funds which is an overall objectives of a business enterprise.Before industrial revolution, finance was not of much importance. The methods of production were simple. For example, the artisan used to work in open small hut. He had simple tools mostly made by himself. Labour at that time was more important than capital and finance did not pose any problem. Production in those days was, therefore labour intensive.World Financial Crisis Not Over
 According to Nouriel Roubini: "The real economy still looks very weak.The US economist widely credited with having predicted the financial crisis has warned we are already "planting the seeds of the next crisis". Nouriel Roubini told the BBC that he is concerned about the growing gap between the "bubbly and frothy" stock markets and the real economy. Over the last six months, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has risen about 45%. But Mr Roubini says he sees an economy where consumers are "shopped out" and "debt burdened".Based on the run up in share prices in recent months, investors appear to be betting that good times are around the corner. A view not shared by Mr Roubini. The crisis is not yet over," the New York University professor said.
According to Nouriel Roubini: "The real economy still looks very weak.The US economist widely credited with having predicted the financial crisis has warned we are already "planting the seeds of the next crisis". Nouriel Roubini told the BBC that he is concerned about the growing gap between the "bubbly and frothy" stock markets and the real economy. Over the last six months, the Dow Jones Industrial Average has risen about 45%. But Mr Roubini says he sees an economy where consumers are "shopped out" and "debt burdened".Based on the run up in share prices in recent months, investors appear to be betting that good times are around the corner. A view not shared by Mr Roubini. The crisis is not yet over," the New York University professor said.I think that there is a growing gap between what is the asset prices and the real economy
"I see an economy where the consumers are shopped out, debt burdened, they have to cut back consumption and save more."The financial system is damaged... and for the corporate sector I don't see a lot of capital spending because there is a glut of capacity."Mr Roubini believes US house prices have further to fall, straining America's fragile recovery.Property prices have already declined sharply. According to the National Association of Realtors, the national median has dropped almost 13% from a year ago to $177,700 (£110,100). Many believe the crises in the residential market could spread to the commercial real estate market causing more headaches for the banks. So where does the "froth" in the markets come from?Mr Roubini - like many other economists - believes it is engineered by the Federal Reserve and the government which has been pumping cash into the economy to dampen the pain of the recession"There is a wall of liquidity chasing assets," he said. "But I think that there is a growing gap between what is the asset prices and the real economy."Although he thinks there will be a correction, he believes some of the mistakes of the past can be avoided if reforms are implemented .
Thursday, December 3, 2009
Breakeven analysis
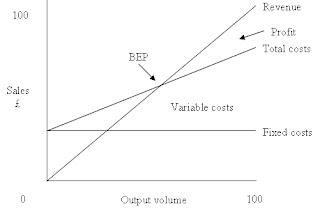 The break-even point for a product is the point where total revenue received equals the total costs associated with the sale of the product (TR=TC).A break-even point is typically calculated in order for businesses to determine if it would be profitable to sell a proposed product, as opposed to attempting to modify an existing product instead so it can be made lucrative. Break even analysis can also be used to analyse the potential profitability of an expenditure in a sales-based business. break even point (for output) = fixed cost / contribution per unit
The break-even point for a product is the point where total revenue received equals the total costs associated with the sale of the product (TR=TC).A break-even point is typically calculated in order for businesses to determine if it would be profitable to sell a proposed product, as opposed to attempting to modify an existing product instead so it can be made lucrative. Break even analysis can also be used to analyse the potential profitability of an expenditure in a sales-based business. break even point (for output) = fixed cost / contribution per unitcontribution (p.u) = selling price (p.u) - variable cost (p.u)
break even point (for sales) = fixed cost / contribution (pu) * sp (pu)
Wednesday, December 2, 2009
Cash flow statement
 In financial accounting, a cash flow statement, also known as statement of cash flows or funds flow statement, is a financial statement that shows how changes in balance sheet and income accounts affect cash and cash equivalents, and breaks the analysis down to operating, investing, and financing activities. The statement captures both the current operating results and the accompanying changes in the balance sheet. As an analytical tool, the statement of cash flows is useful in determining the short-term viability of a company, particularly its ability to pay bills. International Accounting Standard 7 (IAS 7), is the International Accounting Standard that deals with cash flow statements.
In financial accounting, a cash flow statement, also known as statement of cash flows or funds flow statement, is a financial statement that shows how changes in balance sheet and income accounts affect cash and cash equivalents, and breaks the analysis down to operating, investing, and financing activities. The statement captures both the current operating results and the accompanying changes in the balance sheet. As an analytical tool, the statement of cash flows is useful in determining the short-term viability of a company, particularly its ability to pay bills. International Accounting Standard 7 (IAS 7), is the International Accounting Standard that deals with cash flow statements.Investment
 Investment is the active redirection of resources/assets to creating benefits in the future; the use of resources/assets to earn income or profit in the future. It is related to saving or deferring consumption.Investment is involved in many areas of the economy, such as business management and finance no matter for households, firms, or governments. An investment involves the choice by an individual or an organization such as a pension fund, after some analysis or thought, to place or lend money in a vehicle, instrument or asset, such as property, commodity, stock, bond, financial derivatives (e.g. futures or options), or the foreign asset denominated in foreign currency, that has certain level of risk and provides the possibility of generating returns over a period of time.
Investment is the active redirection of resources/assets to creating benefits in the future; the use of resources/assets to earn income or profit in the future. It is related to saving or deferring consumption.Investment is involved in many areas of the economy, such as business management and finance no matter for households, firms, or governments. An investment involves the choice by an individual or an organization such as a pension fund, after some analysis or thought, to place or lend money in a vehicle, instrument or asset, such as property, commodity, stock, bond, financial derivatives (e.g. futures or options), or the foreign asset denominated in foreign currency, that has certain level of risk and provides the possibility of generating returns over a period of time.Investment comes with the risk of the loss of the principal sum. The investment that has not been thoroughly analyzed can be highly risky with respect to the investment owner because the possibility of losing money is not within the owner's control. The difference between speculation and investment can be subtle. It depends on the investment owner's mind whether the purpose is for lending resource to someone else for economic purpose or not.
In the case of investment, rather than store the good produced or its money equivalent, the investor chooses to use that good either to create a durable consumer or producer good, or to lend the original saved good to another in exchange for either interest or a share of the profits. In the first case, the individual creates durable consumer goods, hoping the services from the good will make his life better. In the second, the individual becomes an entrepreneur using the resource to produce goods and services for others in the hope of a profitable sale. The third case describes a lender, and the fourth describes an investor in a share of the business. In each case, the consumer obtains a durable asset or investment, and accounts for that asset by recording an equivalent liability. As time passes, and both prices and interest rates change, the value of the asset and liability also change.
The term "investment" is used differently in economics and in finance. Economists refer to a real investment (such as a machine or a house), while financial economists refer to a financial asset, such as money that is put into a bank or the market, which may then be used to buy a real asset.
Savings Account
 Savings accounts are accounts maintained by retail financial institutions that pay interest but can not be used directly as money ( for example, by writing a cheque). These accounts let customers set aside a portion of their liquid assets while earning a monetary return. Savings accounts are offered by commercial banks, savings and loan associations, credit unions, building societies and mutual savings banks. Some savings accounts require funds to be kept on deposit for a minimum length of time, but most permit unlimited access to funds. In the US, Regulation D, limits the withdrawals, payments, and transfers that a savings account may perform. Banks comply with these regulations differently; some will immediately prevent the transfer from happening, while others will allow the transfer to occur but will notify the account holder upon violation of the regulation. True savings accounts do not offer cheque-writing privileges, although many institutions will call their higher-interest demand accounts or money market accounts "savings accounts."
Savings accounts are accounts maintained by retail financial institutions that pay interest but can not be used directly as money ( for example, by writing a cheque). These accounts let customers set aside a portion of their liquid assets while earning a monetary return. Savings accounts are offered by commercial banks, savings and loan associations, credit unions, building societies and mutual savings banks. Some savings accounts require funds to be kept on deposit for a minimum length of time, but most permit unlimited access to funds. In the US, Regulation D, limits the withdrawals, payments, and transfers that a savings account may perform. Banks comply with these regulations differently; some will immediately prevent the transfer from happening, while others will allow the transfer to occur but will notify the account holder upon violation of the regulation. True savings accounts do not offer cheque-writing privileges, although many institutions will call their higher-interest demand accounts or money market accounts "savings accounts."All savings accounts offer itemized lists of all financial transactions, traditionally through a passbook, but also through a bank statement.
Financial ratio
 In finance, a financial ratio or accounting ratio is a ratio of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. There are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization. Financial ratios may be used by managers within a firm, by current and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and by a firm's creditors. Security analysts use financial ratios to compare the strengths and weaknesses in various companies. If shares in a company are traded in a financial market, the market price of the shares is used in certain financial ratios.
In finance, a financial ratio or accounting ratio is a ratio of two selected numerical values taken from an enterprise's financial statements. There are many standard ratios used to try to evaluate the overall financial condition of a corporation or other organization. Financial ratios may be used by managers within a firm, by current and potential shareholders (owners) of a firm, and by a firm's creditors. Security analysts use financial ratios to compare the strengths and weaknesses in various companies. If shares in a company are traded in a financial market, the market price of the shares is used in certain financial ratios.Ratios may be expressed as a decimal value, such as 0.10, or given as an equivalent percent value, such as 10%. Some ratios are usually quoted as percentages, especially ratios that are usually or always less than 1, such as earnings yield, while others are usually quoted as decimal numbers, especially ratios that are usually more than 1, such as P/E ratio; these latter are also called multiples. Given any ratio, one can take its reciprocal; if the ratio was above 1, the reciprocal will be below 1, and conversely. The reciprocal expresses the same information, but may be more understandable: for instance, the earnings yield can be compared with bond yields, while the P/E ratio cannot be: for example, a P/E ratio of 20 corresponds to an earnings yield of 5%.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
